| REF | DESCRIPTION | SAMPLES PER GEL | TEST PER KIT |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRE610K | ALP ISOENZYMES ELECTROPHORESIS KIT | 13 | 130 |
The ALP electrophoresis kit SRE610K is intended to be used for the qualitative and quantitative identification of the Alkaline Phosphatase isoenzymes in human serum by agarose electrophoresis. Alkaline Phosphatase is an enzyme found in all tissues. Tissues with particularly high concentrations of ALP include the liver, bile ducts, placenta and bone. Damaged or diseased tissue releases enzymes into the blood, so serum ALP measurements can be abnormal in many conditions, including bone disease. To differentiate the location of damaged or diseased tissue in the body, ALP isoenzyme testing must be done. Thanks to the new Pretty Interlab the ALP procedure is extremely fast and user friendly. The kit has been designed for use with the fully automated instruments Easy Interlab G26 & Pretty Interlab.
Reagent Preparation:
All reagents are ready to use, only the NBT must be reconstituted with 2 ml of Substrat.
Sample Preparation:
Each sample must be pre-treated with the Neuraminidase. Distribute 5 μl of Neuraminidase in each well then 25 μl of serum samples. Mix well, wait 5 minutes before starting the analysis
Sample Storage & Stability:
Serum: Fresh serum samples. If needed, 1 week at 2 to 8 °C
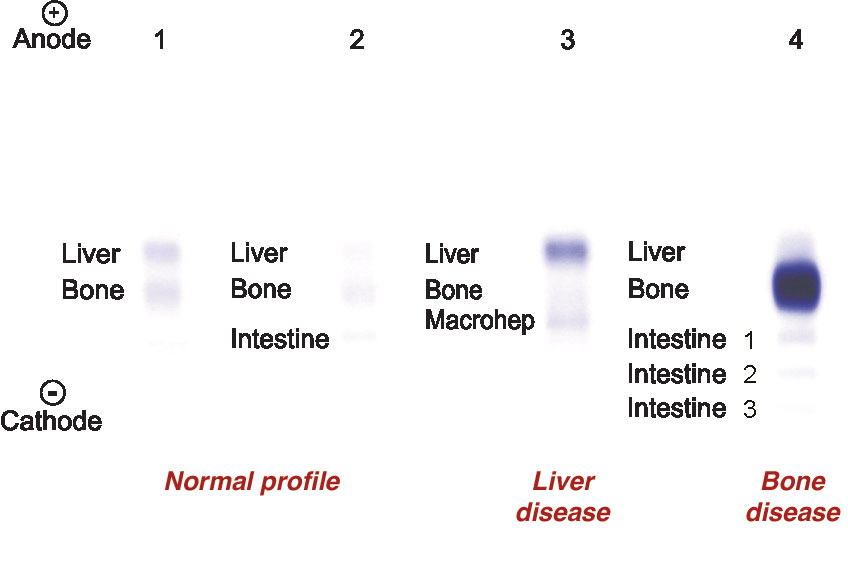
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts performing chemical reactions in the cells of various organs and tissues. Extensive cell leakage may occur due to different factors, causing considerable release of enzymes in the bloodstream. Many enzymes are therefore useful as markers of cellular damage, and the specific measurement of their activity in biological fluids provides a valuable source of information for clinical laboratories. Isoenzymes are multiple forms of the same enzyme, all catalyzing the same reaction but with different rates and substrate specificity. The most important feature of isoenzymes is the tissue/organ specific distribution of each isoform. Therefore the specific increase of one isoform can be correlated to the pathological damage of a given organ or tissue. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP; E.C. 3.1.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the alkaline hydrolysis of a large variety of both naturally occurring and synthetic substrates. This protein is a cell membrane enzyme and is present in almost all tissues of the body, and is prevalent in the bone (osteoblasts), liver, kidney tubules, intestinal epithelium and placenta. ALP seems to be involved in the lipid transport in the intestine and to play an important role in the calcification process in the bone. Several isoforms of ALP exist that can be resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis that, according to the tissue or organ of origin, include: liver (most anodal), bone, macrohepatic, intestinal bands. Analysis of ALP isoenzymes electrophoretic pattern is of particular interest in the investigation of hepatobiliary disease and bone disease. Marked increase of the liver isoform is observed in biliary tree obstruction. Bone ALP increase is correlated to hyperosteoblastic activity in conditions like osteomalacia and bone tumors. Intestinal ALP appears in pathological conditions associated to cirrhosis, diabetes and cancer of the intestinal tract. Additional isoforms are tumor markers and show typical migration rate and chemical and physical characteristics. Special treatment of the sample, either enzymatic and thermal, is required in order to improve the electrophoretic separation of ALP isoforms.
