
| REF | DESCRIPTION | SAMPLES PER GEL | TEST PER KIT |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRE618K | PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS KIT SERUM PROTEINS β۱-β۲ AND CONCENTRATED URINES/CSF | ۶ | ۶۰ | ||
| SRE602K | ۱۳ | ۱۳۰ | |||
| SRE603K | ۲۶ | ۲۶۰ | |||
| SRE637K | ۳۹ | ۳۹۰ |
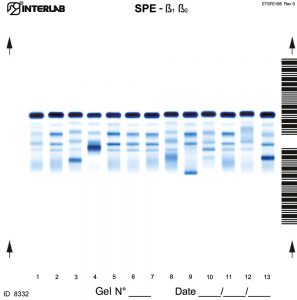
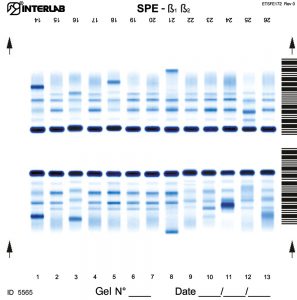
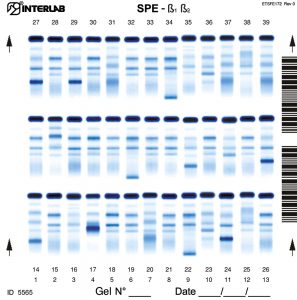
The new kits with enhanced formulation for Serum Protein and Concentrated Urine/ CSF (β۱-β۲ Electrophoresis – SPE) are intended for the separation of proteins in human serum and concentrated urines by electrophoresis on agarose gel plates. Human serum proteins are separated into six distinct, well resolved zones or bands, each containing one or more different proteins. The patterns are examined visually for abnormalities, including variations of the bands or appearance of extra bands. Densitometry of the pattern allows the relative quantification of protein zones. The kits have been designed for use with the fully automated instruments Easy Interlab G26 & Pretty Interlab.
Reagent Preparation:
All reagents ready to use
Sample Preparation:
Neat serum samples. Concentrated urines or CSF to a final total protein concentration ≥ ۲۰ g/L.
Sample Storage & Stability:
Serum: 3 days at 2 to 8 °C Urine/CSF: 1 week at 2 to 8 °C, and 1 month at – ۲۰°C
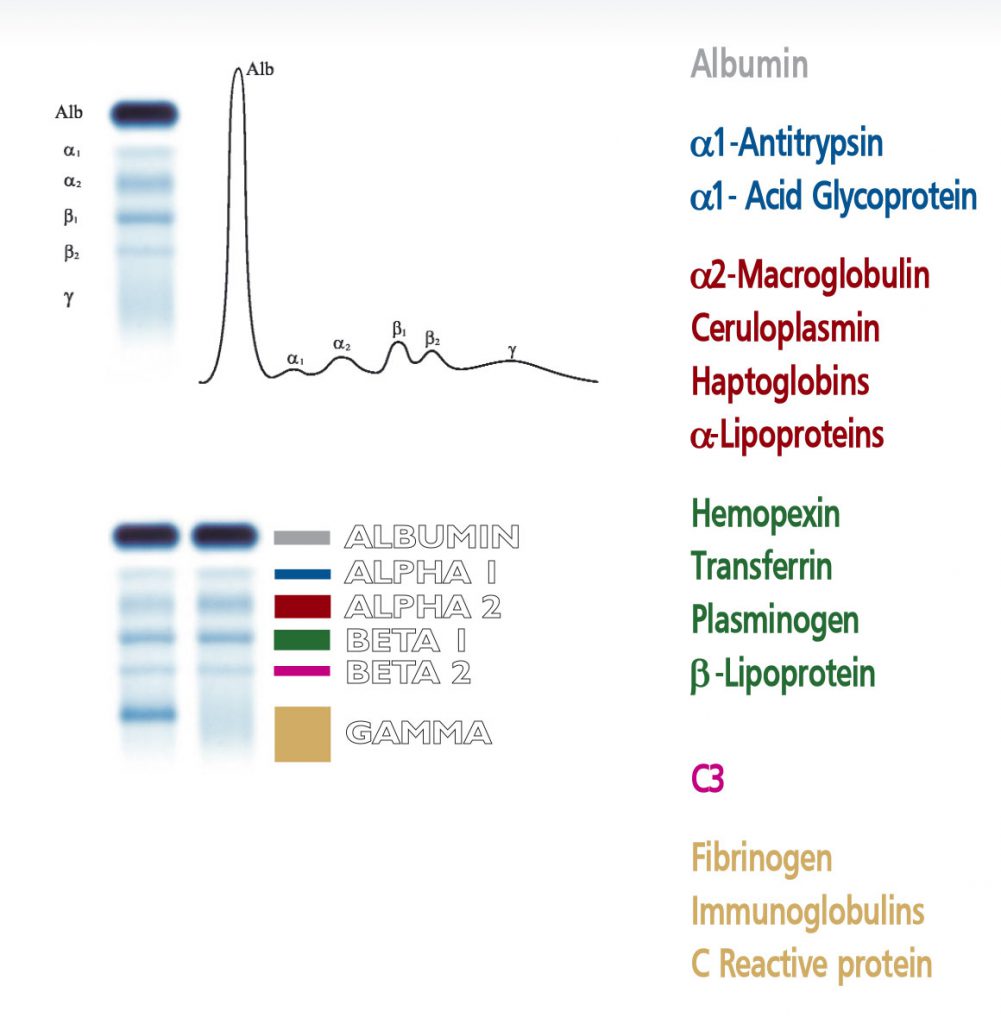
The visual inspection of the electrophoretic pattern of serum proteins on agarose gel plate, may provide useful information on those proteins that are the most representative components of the bands. Any detected variation of the concentration of one or more bands and /or the appearance of additional bands, often paraproteins, have an important clinical meaning (e.g. monoclonal bands, nephrotic syndrome and decreased alpha -1 antitrypsin). Electrophoresis of serum proteins on agarose gel plates for the resolution of b1 and b2 fractions, at alkaline pH, allows to separate six fractions: albumin, alpha 1 (α۱), alpha 2 (α۲), beta 1 (ß۱), beta 2 (ß۲) and gamma (γ).
The beta 1 band consists of transferrin, a protein that plays an important role in the metabolism of iron. Transferrin shuttles ferric ions from intracellular stores to the bone marrow, where the precursor cells of erythrocytes and lymphocytes bear receptors for transferrin on their cell membranes. Various types of transferrin have been described according to their different structural features, all showing beta 1 mobility in the electrophoretic pattern. Splitting of the beta 1 band can be observed due to the presence of paraproteins. In a rare condition the heterozygosis of transferrin produces the splitting of the beta 1 band into two smaller bands that can mimic paraproteins and should be confirmed with differential diagnosis. Splitting of beta 1 band is also observed in transferrin with low content of sialic acid, a condition observed in patients suffering from severe hepatopathy or in alcoholics. Pathological increase of transferrin band is a constant finding in low iron concentration due to anemia. Diminished concentration of transferrin is of poor diagnostic utility and generally reflects diminished hepatic synthesis.
The beta 2 band is associated to the C3 component , a molecule that plays a central role in the complement system, a large group of proteins that trigger inflammation and act as effectors in the lysis of pathogens and phagocytosis of antigens. The visual inspection of the beta 2 band therefore enables to verify the functional activity of this important system. Decrease of C3 is observed in autoimmune diseases (e. g. LES) and rheumathoid arthritis. Another pathological condition associated to a marked decrease of the beta 2 is the post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. C3 component is synthesized in the liver, therefore hepatic diseases may impair the normal synthesis of this protein. Low concentration of C3 may also reflect the genetic condition of reduced expression of the protein. Increased beta 2 band has little clinical value as C3 is an acute phase protein.
