
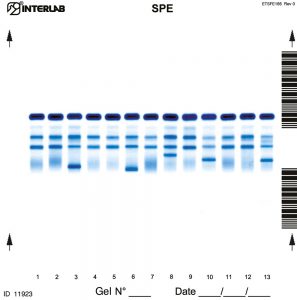
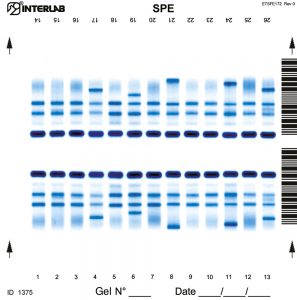
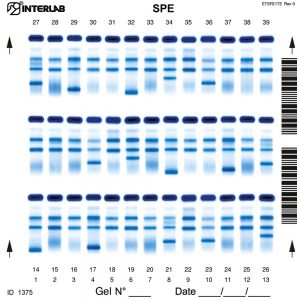
The new kits with enhanced formulation for Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPE) and Concentrated Urines/CSF, are intended for the separation of proteins in human serum and concentrated urines by electrophoresis on agarose gel plates. Human serum proteins are separated into five distinct, well-resolved zones or bands, each containing one or more different proteins. The patterns are examined visually for abnormalities and variations in the separated bands or zones. Densitometry of the patterns allows the relative quantification of protein zones. The kits have been designed for use with the fully automated instruments Easy Interlab G26 & Pretty Interlab.
Reagent Preparation:
All reagents ready to use
Sample Preparation:
Neat serum samples. Concentrated urines or CSF to a final
total protein concentration ≥ ۲۰ g/L.
Sample Storage & Stability:
Serum: 1 week at 2 to 8 °C
Urine/CSF:
۱ week at 2 to 8 °C, and 1 month at – ۲۰°C
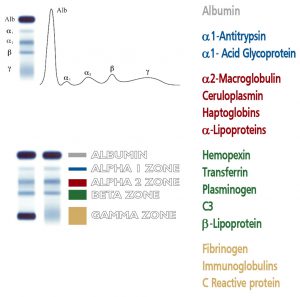
Human body fluids contain a varied mixture of proteins and protein complexes. Each of these protein entities apparently fulfills a specific function in physiological process; furthermore, it is well known that the levels of various proteins in blood serum bear a close relationship to states of health and disease. Of the many techniques available for separating proteins, electrophoresis is a well established and versatile technique, routinely used in clinical laboratories. The most popular method of electrophoretic protein analysis is “zone electrophoresis” on agarose gels. Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPE) performed at pH 8.9 yields five bands: albumin and four globulins (each fraction containing a number of different proteins): alpha 1 (α۱), alpha 2 (α۲), beta (ß), and gamma (γ). Evaluation of single bands by visual inspection provides valuable diagnostic support as it offers a display of the major proteins involved in functional and pathological processes.
The appearance of plasma proteins in the urine (proteinuria) is of great value in the evaluation of renal function. The physiological proteinuria is defined as approximately 150 mg of protein found in a 24 hour urine collection.
Electrophoresis of urine is the best way to detect abnormal proteins in urine.
The presence of an abnormal band requires complementary identification by Immunofixation (for example to assess the presence of a Bence-Jones protein) Abnormal proteins in urine can be present with a normal proteinuria.
