| REF | DESCRIPTION | SAMPLES PER GEL | TEST PER KIT |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRE649K | H.R. PROTEINS ELECTROPHORESIS KIT | ۶ | ۶۰ | ||
| SRE607K | ۱۳ | ۱۳۰ |
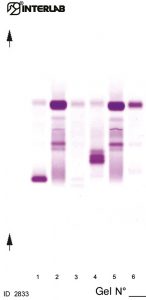
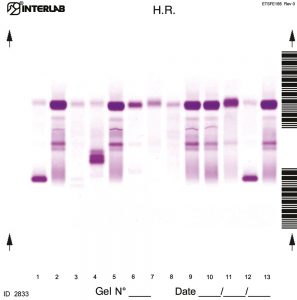
The High Resolution (H. R.) Proteins Electrophoresis kits are intended for the separation of proteins in human serum, urine and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by electrophoresis on agarose gel plates. Proteins are resolved to give an electrophoresis pattern that is examined visually for the detection of abnormal profiles, including both qualitative variations of the bands and appearance of additional bands. This kit allows to run the electrophoresis analysis using neat urine sample. The unique Interlab instruments application method (multiple application) substantially improves the visual inspection and identification of small bands (1.5mg/dl per band). The kits have been designed for use with the fully automated instruments Easy Interlab G26 & Pretty Interlab.
Reagent Preparation:
All reagents ready to use.
Sample Preparation:
Neat urine. Diluted serum 1:20. Concentrated CSF to a final total protein concentration of 10 g/L.
Sample Storage & Stability:
Serum: 1 week at 2 to 8°C, 1 month at -20°C. Urine/CSF: 1 week at 2 to 8°C, and 1 month at –۲۰°C
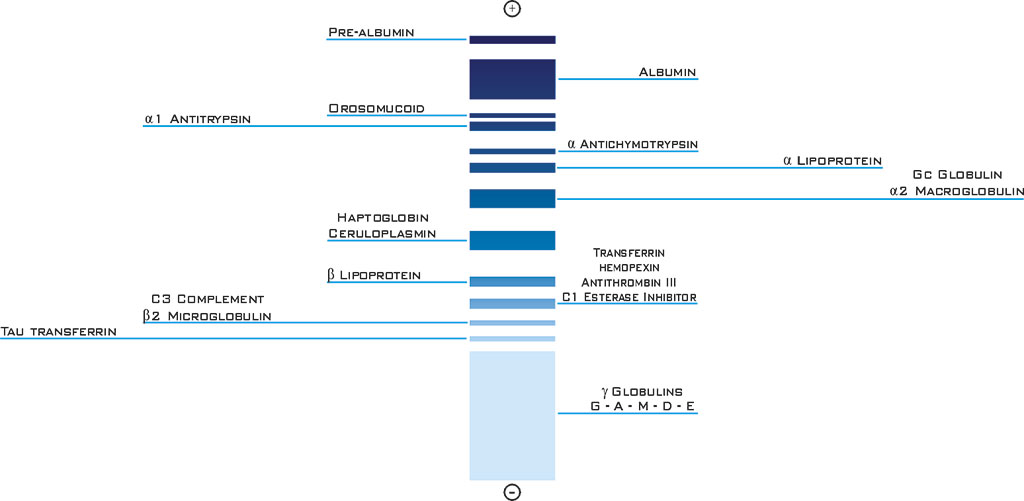
Urine is formed by ultrafiltration of plasma across the glomerular capillary wall that has a sieving effect on larger plasma proteins into the ultrafiltrate. The passage of plasma proteins across the glomerular barrier is dependent upon their molecular size, electrical charge and molecular configuration. All molecules greater than 50,000 daltons are retained by the glomerular barrier. Albumin and transferrin with a molecular weight of 65,000 and 80,000 daltons respectively are almost completely retained, only about 0.1 % of each ultrafiltrates. All the plasma proteins with a molecular mass under 50,000 daltons pass through the glomerular wall, but all are reabsorbed by the proximal tubule cells, and are degraded by enzymes in to amino acids which are returned to the blood.
The final filtrate usually contains some traces of albumin and transferrin (under 0.1% of the total proteinemia). Proteins normally present in urine are albumin and transferrin in low quantity. The physiological proteinuria is about 150 mg of protein found in a 24 hour urine collection. Electrophoresis is the best way to detect abnormal proteins in urines, the presence of an abnormal band (for example a band in the position of the transferrin) requires confirmatory identification (Bence-Jones immunofixation).
The presence of proteins in the 1 and 2 zones, requires further investigation (micro-proteins etc). Abnormal proteins in urine can be present even with a normal level of proteinuria. Immediate analysis of fresh urine is recommended, some proteins can denature in alkaline or in acid urine (for example, ß۲ microglobulin is denaturated at a pH under 5.5, while Retinol Binding Protein (RBP) is denaturated at alkaline pH.
