
| REF | DESCRIPTION | SAMPLES PER GEL | TEST PER KIT |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRE652K | BENCE-JONES IMMUNOFIXATION | ۱ | ۱۰ | ||
| SRE625K | ۲ | ۲۰ | |||
| SRE626K | ۴ | ۴۰ | |||
| SRE640K | ۶ | ۶۰ |
The new Immunofixation of Bence Jones electrophoresis (IFE BJ) kits are intended to be used for qualitative immunological identification of Bence-Jones proteins and for detection of both normal and abnormal proteins in human neat urines. In fact IFE Bence Jones method combines the resolution of protein fractions by electrophoresis with the specific recognition of free light chains using the trivalent antibodiy (GAM, which is a mix of IgG, IgA,and IgM,) raised against heavy chains of human immunoglobulins and their light chains, Kappa and Lambda, both bound and free, plus the only Kappa and Lambda free. Thanks to the new Easy Interlab G26 & Pretty Interlab the Immunofixation procedure is extremely fast and user friendly and in just 45 minutes the first gel is completed. The kits have been designed for use with the fully automated instruments Easy Interlab G26 & Pretty Interlab.
Reagent Preparation:
All reagents ready to use except the washing solution to be diluted 50ml to a final volume of 1L with distilled water.
Sample Preparation:
Neat Urine.
Sample Storage & Stability:
Urine: 1 week at 2 to 8 °C, and 1 month at -20°C
The immunoglobulin molecule is a tetramer containing two heavy chains that define the class (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE) and two light chains, called kappa and lambda respectively. Each immunoglobulin contains a pair of light chains of the same type, either kappa or lambda. Immunoglobulins are synthesized and released in the bloodstream by plasma cells.
Multiple myeloma results from neoplastic proliferation of a single plasma cell clone secreting abnormal amounts of antibody. Mutations in the immunoglobulin genes may result in myeloma cells producing:
· light chains only, a condition called Bence Jones myeloma
· heavy chains only
· molecular fragments of immunoglobulins
The overproduction of this monoclonal protein, present in a variety of shapes and sizes, is common to multiple myeloma and AL amyloidosis. Immunoglobulin free light chains, or Bence Jones proteins, pass from the serum into the urine and are therefore considered the tumor marker for multiple myeloma. Thus, their detection in urine provides valuable information for the initial diagnosis and follow-up. Tests for the screening and the investigation of multiple myeloma also include electrophoretic methods with high sensitivity and specificity for the detection of free light chains.
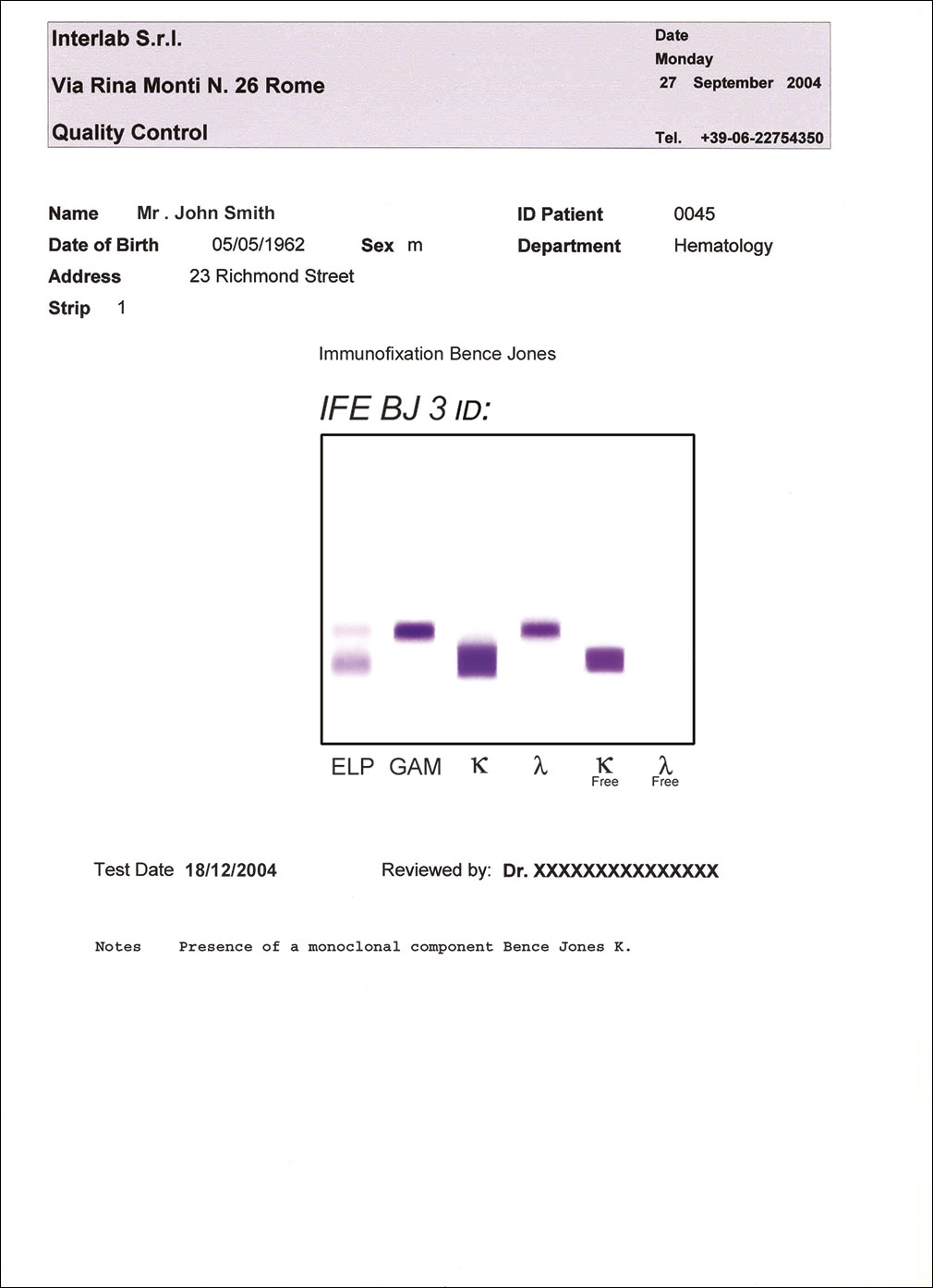
Immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE) is a laboratory method used to define the biochemical identity and homogeneity of immunoglobulins or light chains, when suspected monoclonal components are detected in protein electrophoretic patterns of biological fluids. IFE Bence Jones method combines the resolution of protein fractions by electrophoresis with the specific recognition of free light chains using antibodies raised against heavy chains of human immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, and IgA) and their light chains, kappa and lambda, either bound or free. The binding between the specific antibody and the monoclonal protein, namely the complete immunoglobulin and/or bound and free light chains, results in the formation of a band of precipitate in the corresponding lane that identify the type of immunoglobulin, either heavy chain and/or light chain. The use of Acid Violet, a very sensitive stain for proteins, provides improved quality of the electrophoretic results, for a better visual inspection of the patterns.
